What is SERPs?
Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs) are the dynamic web pages displayed by search engines in response to user queries. These pages act as the bridge between searchers and the vast online content available, organizing results based on relevance, user intent, and sophisticated ranking algorithms. Their primary purpose is to provide users with accurate, ranked, and contextualized information tailored to meet their search needs.
SERPs consist of multiple components, including organic results, paid results, and various interactive features such as featured snippets, knowledge panels, and local packs. These elements offer information in diverse formats—text, images, videos, and real-time updates—making the pages functional, engaging, and efficient for users.
The structure of SERPs is defined by key components like organic listings ranked by relevance and authority, paid advertisements displayed prominently, and rich features such as image packs, video results, and news stories. Interactive tools like People Also Ask (PAA) boxes, related searches, and search filters further enhance user navigation and information discovery.
Beyond these elements, SERPs are shaped by advanced ranking algorithms and personalization techniques. Search engines consider factors like location, search history, and user preferences to tailor results. Features like rich snippets, infinite scroll, and mobile responsiveness ensure that users find relevant content quickly and easily, whether on desktop or mobile devices.
On a technical level, SERPs rely on processes like crawling and indexing, supported by structured data to generate enhanced results. Queries triggering SERPs are categorized as informational, navigational, or transactional, each producing specific layouts. Businesses leverage SERPs for visibility through ad bidding and other monetization strategies, making them a critical space for digital marketing.
Trends such as voice search optimization, AI integration (e.g., BERT, MUM), and the rise of zero-click results are reshaping SERP dynamics. Metrics like search volume, position tracking, impressions, and SERP feature coverage offer valuable insights into performance, while click-through rates (CTR) and bounce rates reflect user engagement.
Navigating through search engine result pages (SERPs) can be tricky for website owners and marketers. It involves dealing with lots of challenges, like understanding different SERP features and keeping up with changes in search results.
There’s also tough competition to be seen, especially on mobile and local searches.
Understanding what users want when they search and dealing with the way content is shown on SERPs makes things even more complex.
For example, imagine you’re trying to find the best fruit in a busy market.
You’d want to know what people are looking for and how to catch their eye. It’s the same online!
Whether it’s understanding what people are searching for or keeping up with changes in how searches work, every decision counts.
There’s lots to consider, from how search results change to the competition for attention, especially in mobile and local searches.
But with a good grasp of how search engines work and some smart strategies, businesses can still shine bright in the online world.
The Structure and Components of SERPs!
SERPs are the pages displayed as a result by search engines when you ask any queries.
Each element, from the search bar to features like featured snippets and knowledge panels, shapes user experience and drives traffic.
Knowing how search engines generate SERPs informs tailored optimization strategies.
This involves on-page and off-page SEO, technical considerations, and tracking with tools like Google Search Console.
Optimizing for local businesses, image and video SERPs, mobile devices, and improving click-through rates are essential components.
Continuous monitoring and optimization can enhance visibility, attract traffic, and achieve business goals.
SERPs are the pages displayed as a result by search engines when you ask any queries. It can help you make your website better by understanding how search engine result pages (SERPs) work, so more people can see it and visit it without you needing to pay for ads.
List of SERPs Components
Here are the common components found in the structure of search engine result pages (SERPs):
Search Bar:
The search bar, typically found at the top of webpages or search engine interfaces, allows users to input their search queries or keywords.
Users can type in what they’re looking for, such as questions or specific terms, and then initiate the search by pressing “Enter” or clicking a search button.
This fundamental component of search engines enables users to access relevant information from the indexed web content.

Search Results:
Search results are the main section of a search engine where relevant information is displayed based on the user’s query.
This includes web pages, images, videos, news articles, and other content that best matches what the user is looking for.
Search results are the listings of content provided by the search engine in response to a user’s search query.
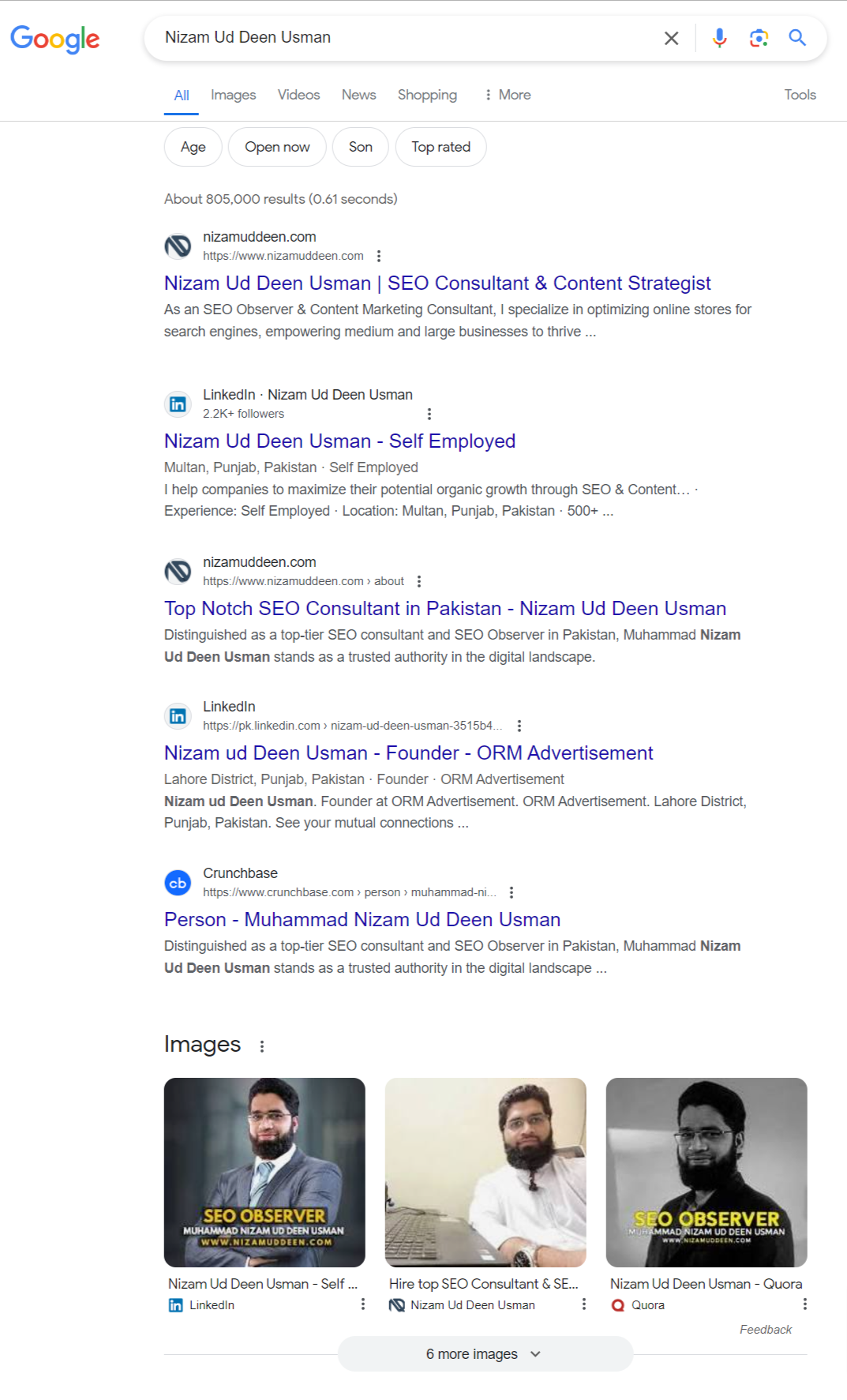
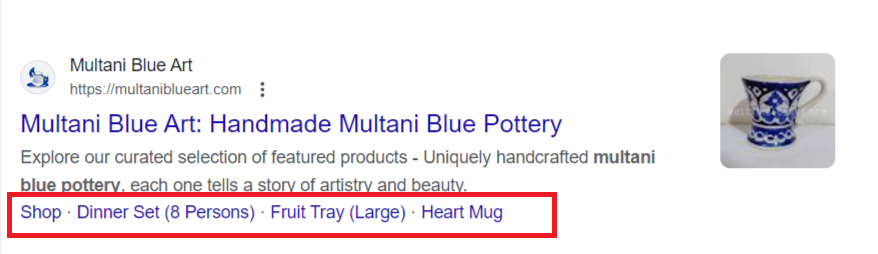
Title Tags:
Title tags are clickable headlines representing the titles of search results, offering a concise description of the content.
They serve as a preview of what the webpage contains, aiding users in deciding which result to click on.
Title tags, found as blue clickable links on SERPs, play a crucial role in attracting users’ attention and improving click-through rates.
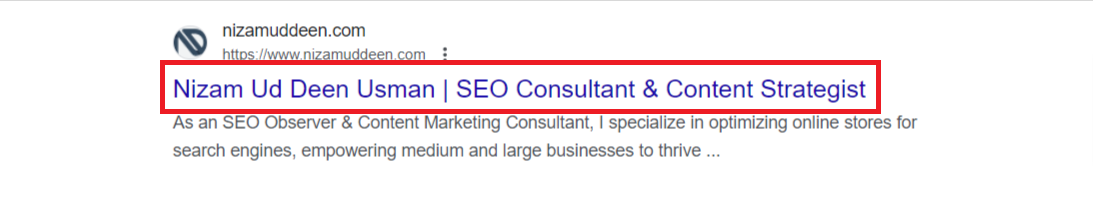
Meta Descriptions:
Meta descriptions provide brief summaries of webpage content, appearing below the title tag in search results.
They offer users a glimpse into what they can expect from the page before clicking on it.
Meta descriptions help users decide which search result is most relevant to their query.
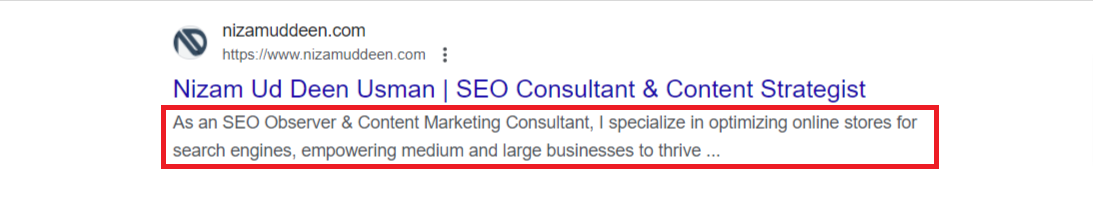
URLs:
URLs, or web addresses, indicate the location of individual web pages on the internet.
They are visible beneath the meta description, serve as navigation aids for users and provide a direct pathway to access the desired webpage.
Users can click on URLs to access specific pages of interest.
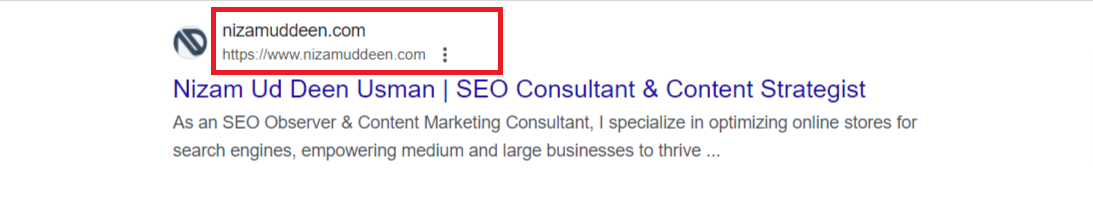
People Also Ask Section:
The “People Also Ask” (PAA) section presents a series of related questions based on the user’s query.
Each question can be expanded to reveal a brief snippet of the answer, allowing users to explore related topics directly within the search results page.
This feature enhances user experience by providing additional information and context related to their original query.
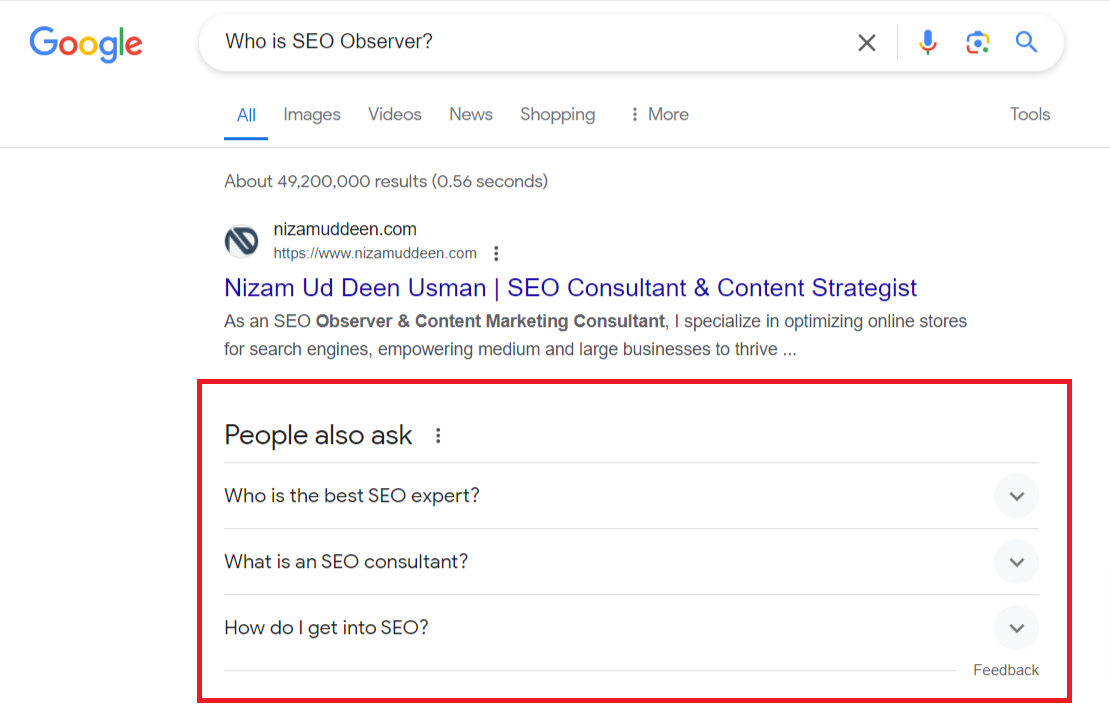
Rich Snippets:
Rich snippets enhance search results by displaying additional information like ratings, reviews, and structured data.
This extra content provides users with more context about the webpage before they click on it.
Rich snippets help users make informed decisions about which search results to choose.
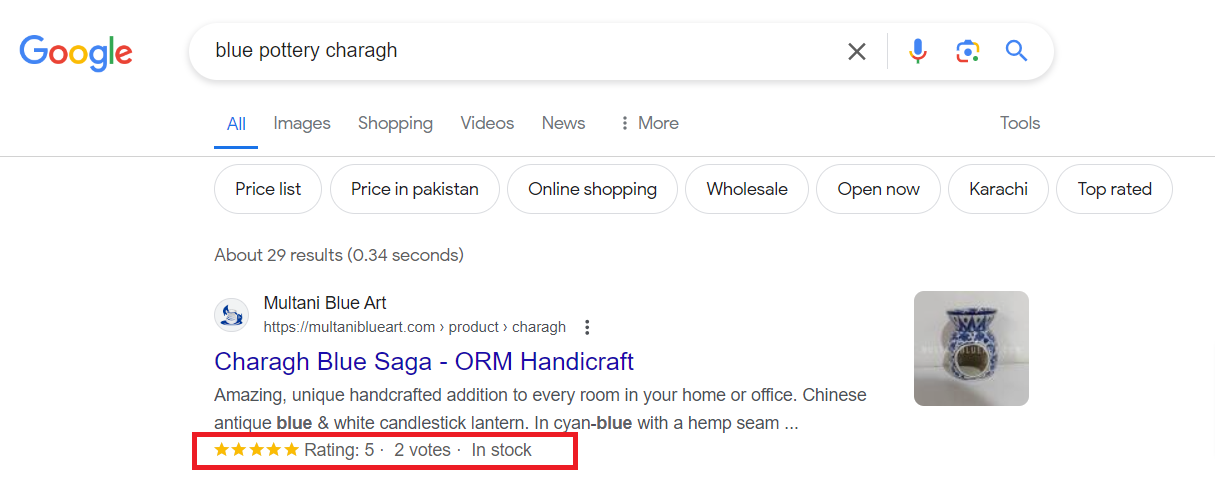
Knowledge Panels:
Knowledge panels offer quick access to information about entities like organizations, people, or places, displayed on the right side of search results.
They provide concise details that users can quickly glance at without navigating away from the search results page.
Knowledge panels enhance the search experience by providing immediate answers to common queries about specific entities.
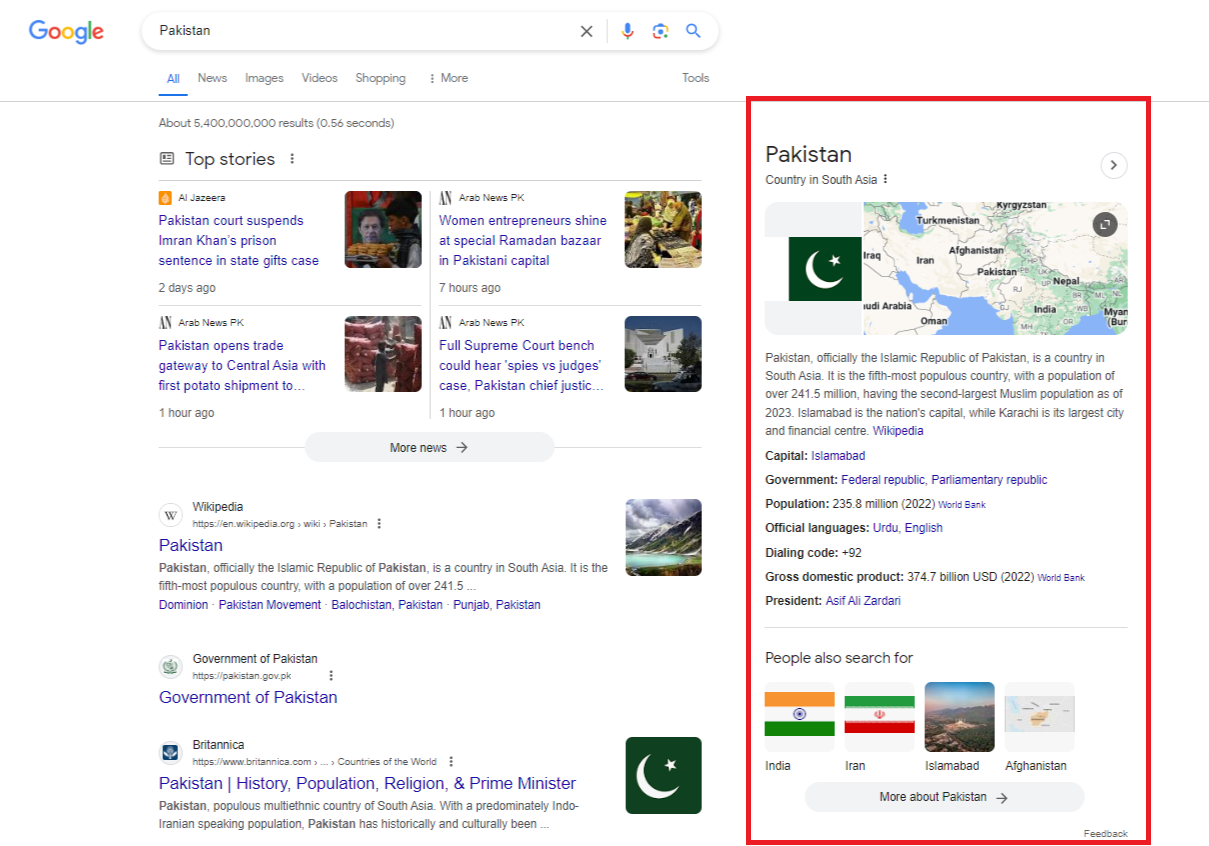
Featured Snippets:
Featured snippets are brief excerpts from web pages that offer direct answers to user queries, prominently displayed at the top of search results.
They provide users with immediate access to relevant information without having to click through to a specific webpage.
Featured snippets enhance user experience by quickly addressing common questions or queries.
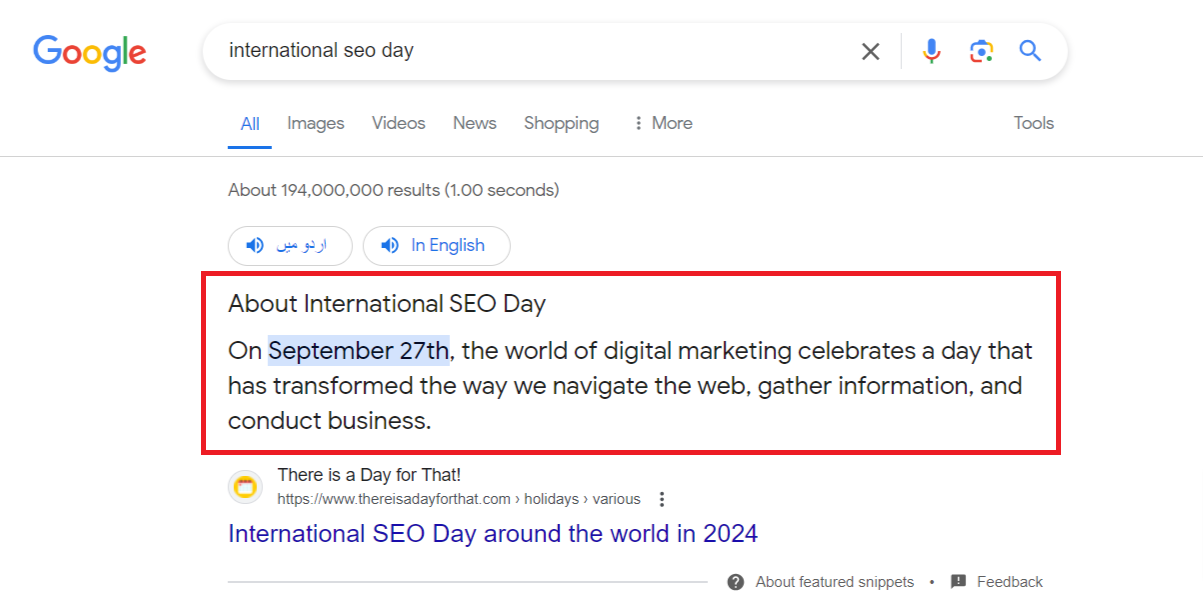
Ad Listings:
Ad listings are paid advertisements marked with an “Ad” label, appearing at the top and bottom of search results.
They are distinct from organic search results and are displayed based on advertisers’ bids and relevance to user queries.
Ad listings allow businesses to promote their products or services to users actively searching for related information.
With Google Ads, advertisers can effectively target their audience and increase visibility through strategic bidding and ad placement.
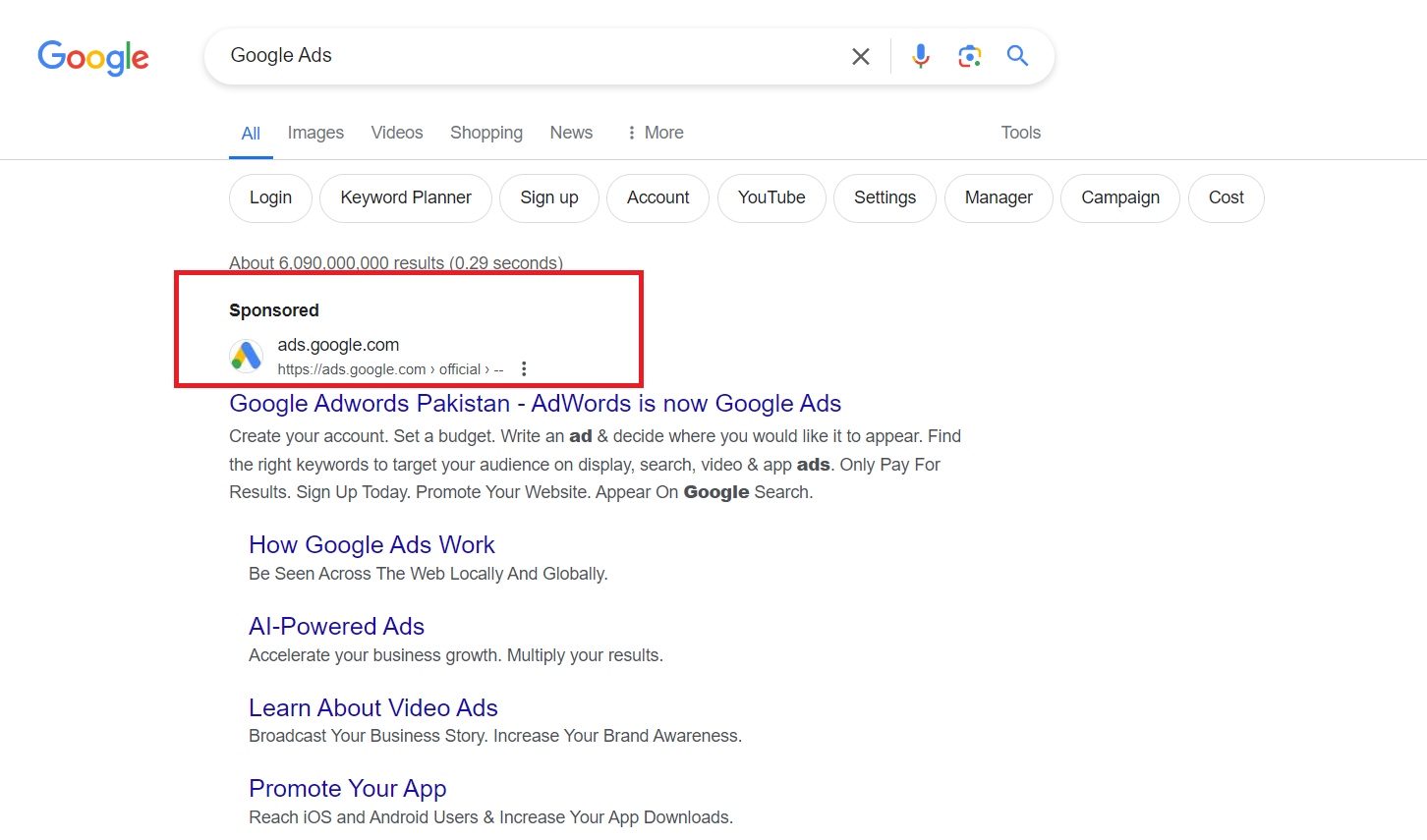
Local Packs:
Local packs showcase a selection of local businesses relevant to a user’s query, along with contact details, ratings, and reviews.
They provide users with quick access to businesses in their vicinity, aiding in local decision-making.
Local packs enhance the search experience for users seeking nearby services or products.
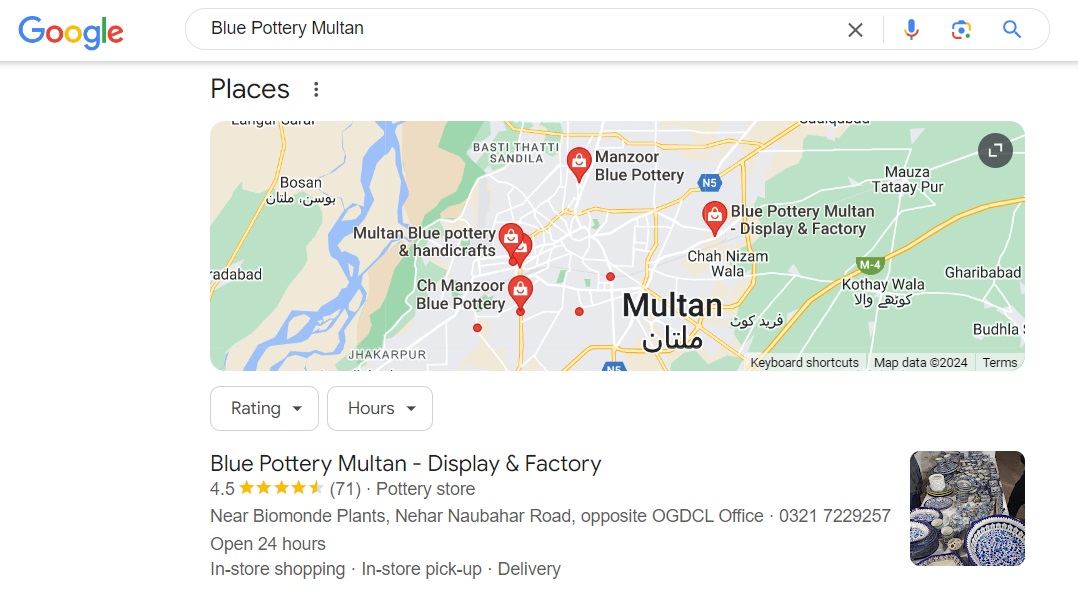
Site Links:
Site links are extra links to specific sections of a website, displayed below the main search result.
They offer users swift access to relevant pages within the site, streamlining navigation.
Site links improve user experience by facilitating easy exploration of different sections of a website directly from the search results page.
Image Carousels:
Image carousels present a collection of images relevant to the user’s search query, allowing them to scroll through directly within the SERP.
They offer visual representation of search results, aiding users in finding relevant content quickly.
Image carousels enhance user experience by providing visual context alongside textual information in the search results.
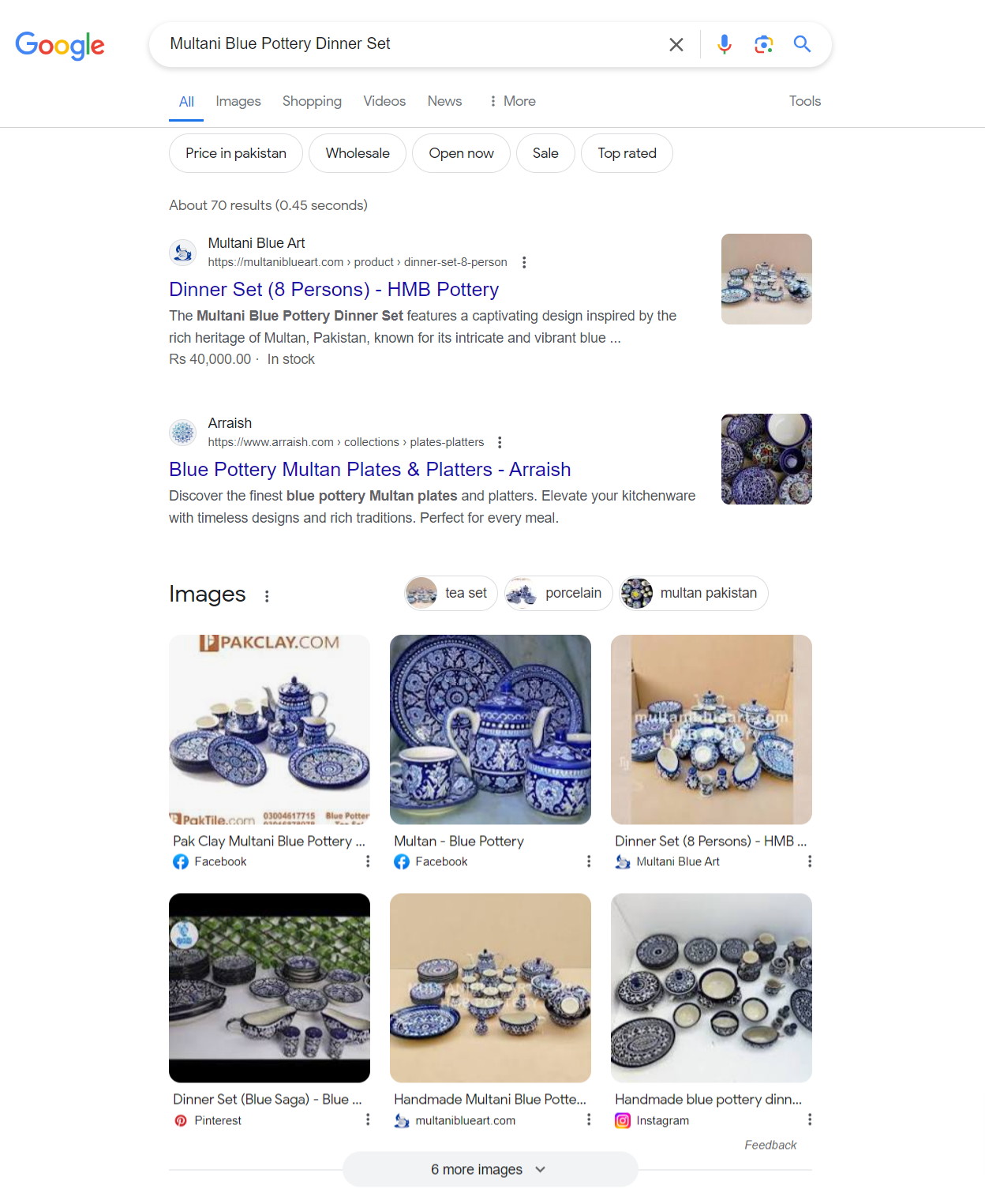
Video Carousels:
Video carousels showcase a series of videos pertinent to the user’s search query, featuring video thumbnails and titles directly within the SERP.
They offer users a convenient way to explore video content without leaving the search results page.
Video carousels enrich the search experience by providing access to relevant video content alongside traditional search results.
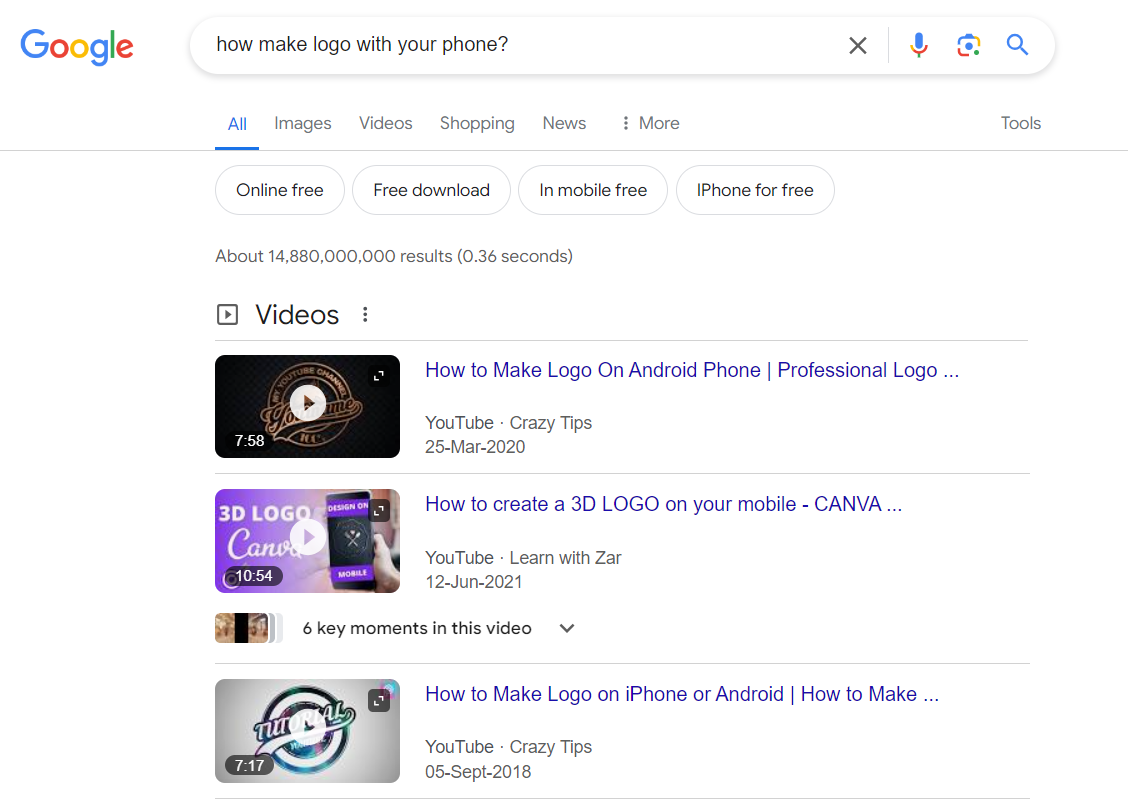
News Results:
News results display recent news articles and updates relevant to the user’s search query, offering access to timely and relevant news information.
They keep users informed about current events and developments related to their search topic.
News results enrich the search experience by providing access to up-to-date news content directly within the search results page.
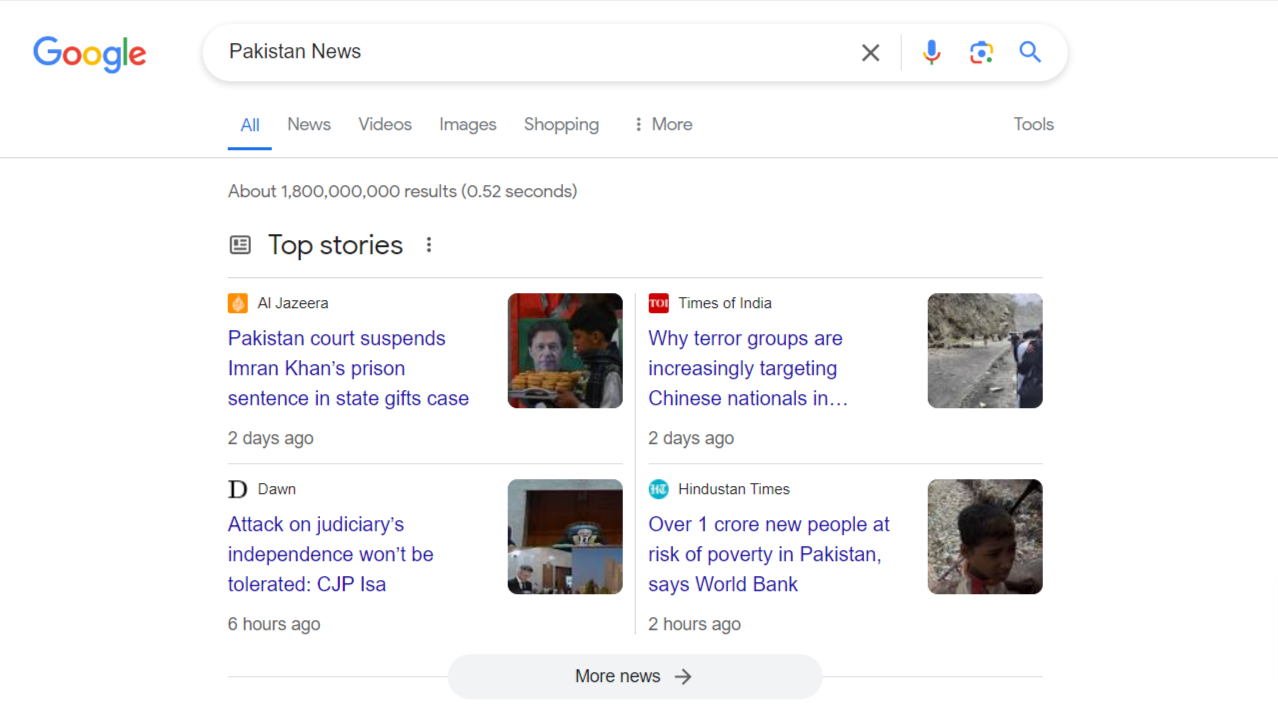
Product Carousels:
Product carousels feature a range of products related to the user’s search query, sourced from e-commerce websites.
Users can browse through product images, titles, and prices directly within the SERP.
They provide a convenient way for users to explore and compare products without leaving the search results page.
Product carousels enhance the search experience by offering quick access to relevant product information.
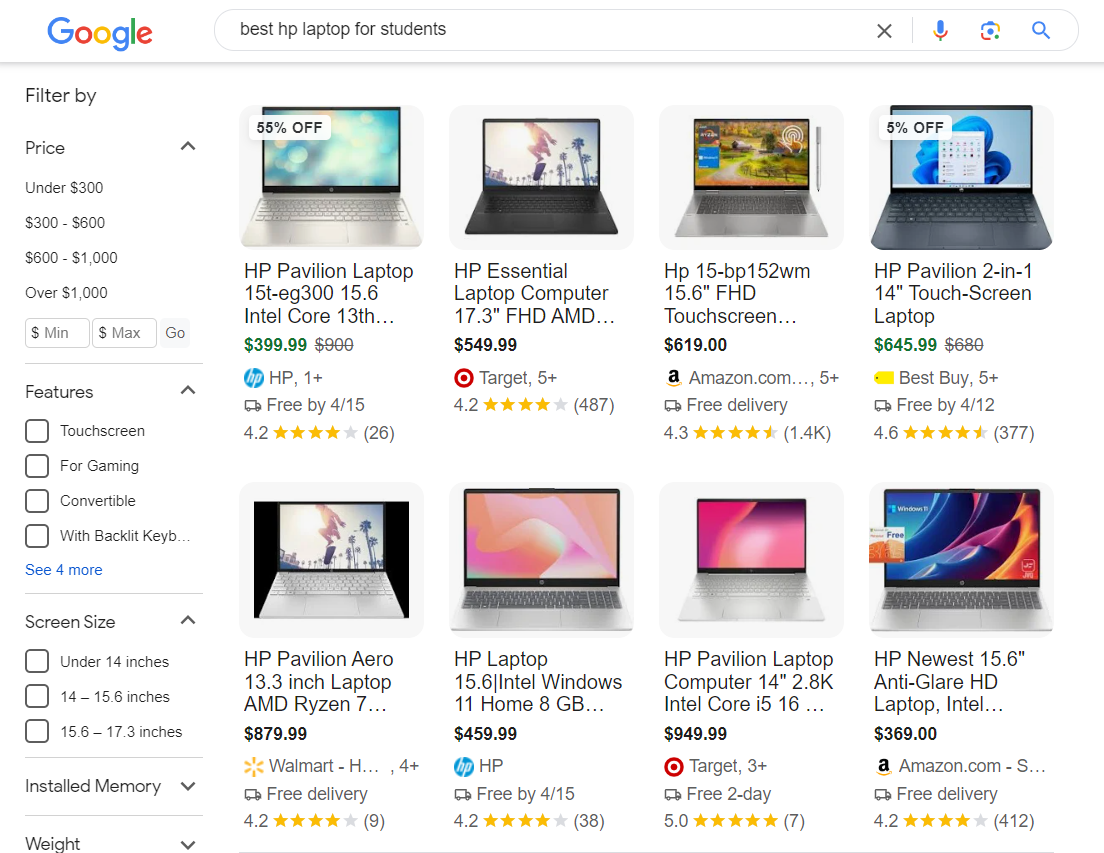
Related Searches:
Related searches display additional search queries related to the user’s original query, appearing at the bottom of the search results page.
They aid users in exploring related topics and discovering additional information of interest.
By offering suggestions for further exploration, related searches enhance the search experience and help users refine their queries.
How Search Engines Generate SERPs?
Have you ever wondered how search engines like Google show you results when you search for something online?
If you understanding this process, which can help you make better use of the internet.
Search engines serve as the gateway to vast repositories of information, efficiently connecting users with relevant content from across the web.
However, the process by which search engines curate and present these results is multifaceted, involving intricate algorithms, continuous indexing of web content, and user-specific personalization.
Let’s explore how search engines generate the results pages you see when you search for something.
Step by Step Process
Search engines generate search engine results pages (SERPs) through a complex process involving several stages.
Let’s find each of them in depth.
First Step is Crawling:
Search engines use special software programs called crawlers or spiders to explore the vast expanse of the internet.
These bots systematically browse through web pages by following links from one page to another. As they navigate the web, they discover new content and continuously index it.
Think of them as internet detectives, always on the lookout for fresh information.
Let’s go deeper into the process of crawling:
- Special Software Programs: Crawlers or spiders are specialized software programs designed by search engines to systematically browse the internet. These bots are programmed to follow links from one webpage to another, essentially mimicking the behavior of a human user clicking on links.
- Systematic Browsing: Crawlers traverse the web in a methodical manner, starting from a set of seed URLs (uniform resource locators) provided by the search engine. They begin by visiting these seed URLs and then follow links found on those pages to discover new content.
- Following Links: As crawlers encounter links on a webpage, they follow those links to other pages, creating a vast network of interconnected web pages. This process continues recursively, with crawlers moving from one page to another, following links along the way.
- Discovering New Content: Through this process of following links, crawlers discover new web pages that they have not encountered before. This allows search engines to continuously discover and index new content as it is published on the internet.
- Continuous Indexing: As crawlers visit web pages, they extract information from those pages and add it to the search engine’s index. This index is essentially a massive database containing information about the content of web pages, including text, images, videos, and other media.
- Frequency of Crawling: Search engines employ algorithms to determine how frequently to crawl a website. Popular websites with frequently updated content may be crawled more frequently, while less popular or static websites may be crawled less often.
- Respecting Robots.txt: Websites can provide instructions to crawlers through a file called robots.txt, which specifies which pages should or should not be crawled. Crawlers typically respect these directives to ensure they only index content that website owners want to be indexed.
- Crawl Budget: Search engines also allocate a certain “crawl budget” to each website, which determines how many pages from that site will be crawled during each visit. This helps ensure that crawlers focus their efforts on the most important and relevant pages.
In essence, the crawling process is the foundation of how search engines discover and index web content, allowing them to build a comprehensive index of the internet’s vast information landscape.
Second Step is Indexing:
Once the crawlers find a webpage, search engines index its content. Indexing involves analyzing the text, images, videos, and other media on the page.
Search engines then organize this information in their databases, making it easier to retrieve when users search for relevant topics. It’s like creating a massive library catalog, categorizing each book based on its contents.
Let’s me explain the process of indexing in more detail:
- Analyzing Content: When crawlers discover a webpage, they don’t just visit it; they also analyze its content. This involves extracting and processing various elements, including text, images, videos, metadata, and other media present on the page.
- Text Analysis: Crawlers extract the textual content of the webpage, including titles, headings, paragraphs, and other textual elements. They analyze this text to understand the main topics, keywords, and themes covered on the page.
- Image and Video Processing: In addition to text, crawlers also analyze multimedia content such as images and videos. This may involve extracting metadata associated with these media files, such as alt text for images or descriptions for videos.
- Metadata Extraction: Crawlers collect metadata associated with the webpage, including information such as the page title, meta description, authorship details, publication date, and more. This metadata provides additional context about the content of the page.
- Language and Encoding Detection: Search engines employ language and encoding detection algorithms to identify the language of the webpage’s content and ensure proper handling of non-standard character encodings.
- HTML Parsing: Crawlers parse the HTML structure of the webpage to understand its layout and structure. They identify important elements such as headers, paragraphs, lists, and links, which help determine the hierarchical structure of the content.
- Indexing Process: Once the content of the webpage has been analyzed, search engines add it to their index—a massive database containing information about the content of web pages. This indexing process involves categorizing the content based on its topics, keywords, relevance, and other factors.
- Data Organization: Search engines organize the indexed data in their databases using sophisticated algorithms. This organization enables efficient retrieval of relevant information when users search for specific topics or keywords.
- Ranking Signals: In addition to indexing content, search engines may also assign ranking signals to web pages based on various factors such as relevance, authority, freshness, and user engagement. These signals help determine the position of web pages in search results.
In essence, indexing is the process of analyzing and organizing the content of web pages so that search engines can efficiently retrieve and present relevant information to users when they perform search queries.
The Last Step is Ranking:
When you type a query into a search engine, it scours its index to find the most relevant pages. But how does it decide which pages to show first?
That’s where ranking algorithms come into play.
Search engines use complex algorithms to evaluate the relevance, authority, and user experience of each page. Pages that meet these criteria are ranked higher and displayed prominently in the search results.
Let’s go deeper into the process of ranking in search engine results:
- Query Understanding: When a user enters a search query, the search engine first seeks to understand the intent behind the query. This involves analyzing the keywords used, context, and user location to provide the most relevant results.
- Index Retrieval: Once the search engine understands the query, it retrieves relevant pages from its index. The index contains a vast database of web pages that have been crawled, analyzed, and categorized based on their content.
- Relevance Assessment: The search engine evaluates the relevance of each indexed page to the user’s query. It looks for pages that contain the keywords in the query and assesses their topical relevance to determine if they are likely to provide valuable information to the user.
- Authority Evaluation: In addition to relevance, the search engine assesses the authority of each page. Authority is determined by factors such as the number and quality of inbound links (backlinks) pointing to the page, the reputation of the website, and the expertise of the content creators.
- User Experience Consideration: Search engines also take into account the user experience provided by each page. Factors such as page load speed, mobile-friendliness, and the presence of intrusive ads or pop-ups can impact the user experience. Pages that offer a seamless and engaging user experience are favored in rankings.
- Algorithmic Analysis: Search engines use complex algorithms to weigh these various factors and calculate a numerical score or ranking for each page. These algorithms are continuously refined and updated to improve the relevance and quality of search results.
- Ranking Adjustment: Once the ranking scores are calculated, search engines sort the pages in order of relevance and authority. Pages that meet the criteria for relevance, authority, and user experience are ranked higher and displayed prominently in the search results.
- Personalization: In some cases, search results may be personalized based on factors such as the user’s search history, location, and previous interactions with search results. Personalized results aim to provide a more tailored and relevant search experience for individual users.
Overall, the process of ranking in search engine results involves a sophisticated evaluation of relevance, authority, and user experience to determine the most valuable and helpful pages for a given query.
The End is Displaying Results:
Once the search engine has ranked the pages, it assembles them into a search engine results page (SERP).
This page typically includes a mix of organic search results, paid advertisements, and additional features like featured snippets, knowledge panels, and related searches.
The goal is to provide users with a diverse array of information that best matches their query.
Let’s explore the process of displaying results in more depth:
- Organic Search Results: Organic search results are the primary listings that appear on a SERP. These results are determined by the search engine’s ranking algorithms, which assess the relevance and authority of web pages based on the user’s query. Organic results are typically displayed in a list format, with each result consisting of a title, URL, and meta description.
- Paid Advertisements: Paid advertisements, also known as sponsored results or paid listings, are displayed prominently on a SERP. These ads are typically marked with labels such as “Ad” or “Sponsored” to distinguish them from organic results. Advertisers bid on keywords relevant to their products or services, and their ads are displayed when users search for those keywords. Paid ads often appear at the top or bottom of a SERP, as well as in the sidebar.
- Featured Snippets: Featured snippets are special results that are displayed prominently at the top of some SERPs. These snippets provide concise answers to user queries, often extracted from the content of web pages. Featured snippets aim to provide users with immediate answers to their questions without requiring them to click through to a specific website. They typically appear in a box format above the organic search results.
- Knowledge Panels: Knowledge panels are informational boxes that appear on the right side of a SERP for certain queries. These panels provide detailed information about specific topics, entities, or organizations, sourced from various trusted databases and websites. Knowledge panels aim to provide users with quick access to relevant information without having to visit multiple websites.
- Related Searches: Related searches are suggestions provided at the bottom of a SERP, offering additional search queries related to the user’s original query. These suggestions help users explore related topics or refine their search queries to find more relevant information. Related searches are based on common queries and user behavior, aiming to assist users in finding the information they need more efficiently.
So, the full overview of this step is already explained above in details, scroll up and learn more about each of displaying result of SERPs.
Another Secret Recipe is Personalization:
Search engines strive to personalize the search experience for each user. They take into account factors such as your search history, location, device, and previous interactions with search results.
Search engines aim to deliver the most relevant and useful information to you by tailoring the results to your individual preferences and interests.
Here’s a more in-depth explanation of how personalization works:
- Search History: Search engines track your search history to understand your interests and preferences. They analyze the topics and types of content you frequently search for, as well as the websites you visit from search results. Search engines can personalize future search results to better match your interests by understanding your search history.
- Location: Your location provides valuable context for search engines to deliver relevant results. Search engines can use your IP address or GPS coordinates to determine your location and customize search results based on local information such as nearby businesses, events, and attractions. For example, if you search for “restaurants,” search engines may prioritize results for restaurants in your vicinity.
- Device: Search engines take into account the device you’re using to conduct a search. Results may be formatted differently for desktop computers, smartphones, and tablets to optimize the user experience. Additionally, search engines may consider factors such as screen size and input method (e.g., touchscreen vs. keyboard) when personalizing search results.
- Previous Interactions: Search engines track your interactions with search results, including which links you click on and how long you spend on a particular page. This data helps search engines understand your preferences and interests more accurately. For example, if you frequently click on articles from a particular website, search engines may prioritize that website’s content in future search results.
- User Preferences: Some search engines allow users to customize their search preferences, such as language settings, safe search filters, and preferred search providers. These preferences are taken into account when personalizing search results to ensure they align with the user’s preferences.
Overall, personalization enables search engines to deliver more relevant and useful search results by considering factors such as search history, location, device, previous interactions, and user preferences.
Understand the Search Intent!
Search intent, also known as user intent or query intent, refers to the underlying motivation behind a user’s online search query. It encompasses the reason why a user is conducting a search and what they hope to achieve or find through their search query.
By deciphering search intent, you can align your content and website strategy to meet the needs of search engine users.
Let’s learn in depth to handle your target audience effectively.
Different Types of Search Queries
Search queries can be categorized into different types based on the intent of the user.
When you understand the various types of search queries, it helps in creating content that aligns with the user’s intent and provides relevant information.
Here are three common types of search queries:
Navigational Queries:
Navigational queries occur when users are searching for a specific website or web page.
Users already have a particular destination in mind and use search engines to find the correct website or navigate to a specific webpage.
Here are examples of navigational queries:
- Query: “Facebook login” Intent: The user wants to access their Facebook account.
- Query: “Amazon” Intent: The user intends to visit the Amazon website to shop for products.
- Query: “YouTube” Intent: The user is looking to access the YouTube platform to watch videos.
Navigational queries typically involve users searching for specific websites, brands, or online platforms they already know or have in mind. They use search engines to quickly navigate to the desired destination.
Informational Queries:
Informational queries involve users seeking information or answers to their questions. They are looking for knowledge, facts, explanations, or solutions to a problem.
Content that addresses informational queries should focus on providing comprehensive and helpful information.
Here are examples of Informational queries:
- A user searches for “best ways to lose weight” to find tips and strategies for achieving weight loss goals.
- Someone types “history of the Roman Empire” to learn about the rise and fall of ancient Rome.
- A user queries “how does solar energy work” to understand the process of harnessing solar power for electricity generation.
In each example, users seek information or answers to their questions, indicating an informational query. They are looking for knowledge, facts, explanations, or solutions to a particular topic or problem.
Transactional Queries:
Transactional queries indicate users’ intent to perform a specific action, such as making a purchase, downloading a file, or signing up for a service.
Users are typically ready to engage in a transaction or conversion, and content should cater to their needs accordingly.
Here are examples of Transactional queries:
- A user searches for “buy iPhone 13” to find options for purchasing the latest iPhone model online.
- Someone types “book flight to Paris” to search for and book a flight ticket to Paris for an upcoming trip.
- A user queries “download Microsoft Word” to find a link to download the Microsoft Word application for document processing.
In each example, users express their intent to perform a specific action, whether it’s making a purchase, booking a flight, or downloading a software application. They are ready to engage in a transaction or conversion, and content should cater to their needs accordingly.
Optimizing for SERPs
Optimizing for search engine results pages is essential for increasing your online visibility and attracting organic traffic to your website.
You can improve your website’s ranking in search engine results and ensure that it appears prominently for relevant queries by implementing strategic techniques and best practices.
Optimizing for SERPs involves a multifaceted approach, from optimizing on-page elements such as title tags and meta descriptions to enhancing website performance and user experience.
This strategy aims to maximize your website’s visibility and relevance in search engine results.
On-Page SEO Factors
On-page SEO refers to optimizing elements directly on the web page to improve its visibility and relevance to search engines.
Consider the following factors when optimizing for SERPs:
Keyword Research and Optimization:
Conduct thorough keyword research to identify the terms and phrases users are searching for.
Optimize your content by incorporating these keywords naturally into headings, paragraphs, image alt tags, and meta tags to help search engines understand the relevance of your page to specific queries.
Content Quality and Relevance:
Create high-quality, informative, and engaging content that satisfies the user’s search intent.
Ensure your content is comprehensive, well-structured, and offers unique value to users.
Use headings, subheadings, and bullet points to enhance readability and make it easier for search engines to crawl and understand your content.
Meta Tags Optimization:
Optimize meta tags, including the title tag and meta description, to accurately reflect the content on your page.
Write compelling and concise title tags that include relevant keywords and entice users to click on your link.
Craft meta descriptions that provide a clear summary of your page’s content and encourage users to visit your website.
Off-Page SEO Factors
Off-page SEO focuses on activities outside of your website that can influence its visibility and reputation.
Consider the following factors when optimizing off-page elements:
Link Building & Outreach:
Earn high-quality backlinks from reputable websites that are relevant to your industry or niche.
Backlinks act as endorsements for your content, signaling to search engines that your website is trustworthy and authoritative.
Engage in outreach, guest blogging, and social media promotion to acquire valuable backlinks.
Social Signals:
Establish a strong presence on social media platforms and encourage social sharing of your content.
Likes, shares, and comments on social media indicate user engagement and can indirectly impact your website’s visibility in search results.
Technical SEO Considerations
Technical SEO focuses on optimizing the technical aspects of your website to improve its crawlability, indexability, and overall performance.
Consider the following technical factors:
Website Speed and Performance:
Optimizing for SERPs involves a multifaceted approach, from optimizing on-page elements such as title tags and meta descriptions to enhancing website performance and user experience.
This strategy aims to maximize your website’s visibility and relevance in search engine results.
Mobile-Friendliness:
With the increasing use of mobile devices, it is essential to have a mobile-friendly website. Responsive design, mobile-friendly layouts, and easy navigation on mobile devices contribute to better user experience and search engine rankings.
You can improve your website’s visibility in search engine result pages (SERPs) by optimizing these on-page, off-page, and technical factors.
Tracking and Analyzing SERPs
Tracking and analyzing search engine result pages (SERPs) is a fundamental aspect of effective search engine optimization (SEO) and digital marketing. By monitoring and understanding SERPs, you can gain valuable insights into your website’s performance, keyword rankings, and competitor analysis.
We will learn the importance of tracking and analyzing SERPs, and discuss the tools and techniques available for this purpose, and highlight the key metrics to focus on.
Tools for Monitoring SERP Performance
Tracking and analyzing the performance of your website in SERPs is crucial to understanding the effectiveness of your SEO efforts.
Several tools can help you monitor and gather data on SERP performance, including:
Google Search Console:
Google Search Console provides valuable insights into how your website appears in search results. It offers data on search queries, impressions, clicks, and average position.
You can also identify crawl errors, submit sitemaps, and monitor your website’s indexing status.
SEO Analytics Platforms:
Various SEO analytics platforms, such as:
these provide comprehensive data and reporting on keyword rankings, organic traffic, backlink profiles, and competitor analysis.
These tools help you track your website’s performance and identify areas for improvement.
Key Metrics to Measure
When analyzing SERP performance, consider the following key metrics:
Organic Rankings:
Monitor the rankings of your target keywords to understand how well your website is positioned in search results.
Track changes in rankings over time and identify opportunities to improve.
Click-Through Rates (CTRs):
Measure the percentage of users who click on your website’s link in search results.
High CTRs indicate that your title tags and meta descriptions are compelling and enticing users to visit your website.
Search Engine Market Share:
Analyze the distribution of organic traffic from different search engines.
You should understand the market share of search engines that can help you prioritize optimization efforts and target the platforms that generate the most traffic.
Monitoring these metrics allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of your SEO strategies, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions to enhance your website’s visibility and performance in SERPs.
SERP Features and Rich Snippets
SERP features and rich snippets are key elements that enhance the visibility and click-through rates of search engine result pages. These features provide users with quick access to relevant information directly on the search results page, offering a more dynamic and interactive search experience.
Here, I will explain the various types of SERP features and rich snippets, their impact on website visibility. And strategies to optimize your content to appear in these enhanced search results.
What are SERP Features? How to Optimize for them?
SERP features are elements displayed on search engine result pages that provide additional information and enhance the user experience.
I am going to help you understand and teach you how to optimize for SERP features that can significantly impact your website’s visibility and attract more clicks.
Consider the following aspects of featured snippets:
- Featured snippets come in different formats like paragraphs, lists, tables, and videos, tailored to match the user’s query and available information.
- Being featured in a snippet boosts your website’s visibility and credibility, positioning it as a trustworthy source of information.
- Appearing in a featured snippet increases the likelihood of attracting organic clicks and driving valuable traffic to your website.
Here are some common SERP features you can learn to optimize:
Featured snippets Optimization:
Concise summaries at the top of search results, providing quick answers to user queries and linking to the source page.
Optimize content with structured answers to target featured snippet opportunities.
Featured snippets optimization involves the following method:
Crafting Concise Summaries:
To optimize for featured snippets, create content that provides clear and succinct answers to commonly asked questions related to your topic.
Organize your content in a format that aligns with common featured snippet types, such as paragraphs, lists, tables, or bullet points.
Use headers, bullet points, or numbered lists to present information in a clear and organized manner.
For Example:
If you’re writing a blog post about the benefits of meditation, include a section that answers common questions such as ‘What are the benefits of meditation?‘ or ‘How does meditation reduce stress?‘
Keep your answers clear and succinct, providing valuable information in a concise manner.
This makes it easier for search engines to identify and display your content as a featured snippet.
Knowledge Panels Optimization:
Display information about entities (organizations, people, places) on the right side of search results.
Optimizing structured data increases the chance of appearing in knowledge panels.
To optimize for Knowledge Panels:
- Implement schema.org markup on your website to provide detailed information about entities. Tag data elements like names, addresses, contact details, and descriptions.
- Ensure accuracy and comprehensiveness of entity information, including business hours, contact details, location maps, and social media profiles. Rich and detailed information boosts chances of being featured.
- Publish authoritative content showcasing expertise, achievements, or contributions related to the entity. Quality content establishes credibility and authority, increasing chances of being featured.
- Encourage positive reviews and endorsements from reputable sources. External validation enhances entity reputation and likelihood of being showcased in Knowledge Panels.
- Keep entity information and content up-to-date to maintain relevance and improve chances of being featured in Knowledge Panels.
You can improve your chances of appearing in Knowledge Panels and provide users with valuable information about your entity directly in search results by following these optimization methods.
Rich Snippets and Structured Data Markup Optimization
Rich snippets provide additional context and visual enhancements to search results. They can include star ratings, product prices, event dates, recipe details, and more.
Implementing structured data markup on your website helps search engines understand the content and display rich snippets.
To optimize for Rich Snippets you can follow these steps:
- Determine which types of rich snippets are relevant to your content, such as reviews, recipes, events, or product information.
- Use schema.org markup to annotate your content with structured data. This helps search engines understand the context and meaning of your content, making it eligible for rich snippets.
- Follow best practices for implementing structured data markup, including using the appropriate schema types, providing accurate and detailed information, and testing your markup with Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool.
- Monitor the performance of your rich snippets in search results using Google Search Console. Make adjustments as needed to improve visibility and click-through rates.
- Regularly review and update your structured data markup to ensure it accurately reflects the content on your website.
You can enhance the visibility and attractiveness of your search results, leading to increased click-through rates and improved organic traffic by optimizing for rich snippets and structured data markup.
SERP Optimization for Local Businesses
With the increasing reliance on search engines to find nearby products and services, optimizing for local search has become essential for businesses targeting a geographically specific audience.
GMB management, and acquiring positive reviews, businesses can improve their rankings in local search results by implementing strategic techniques such as local keyword optimization.
This helps them attract more customers from their target area.
Local SEO Factors and Considerations
Show local businesses relevant to a query, including contact details, ratings, and reviews.
If you optimize Google Business listing, acquire positive reviews, and use relevant local keywords then the chances are high to appear in local packs for location-based queries.
To optimize for Local Packs you need to follow these few steps:
- Claim and update your GMB listing with accurate business information.
- Encourage happy customers to leave positive reviews on GMB and other review platforms.
- Incorporate relevant local keywords into your website and content.
- Make sure your website is mobile-friendly for users searching on smartphones.
- Display your business address prominently on your website.
- Ensure that your business name, address, and phone number (NAP) are consistent across all online platforms.
- Build backlinks from local directories, chambers of commerce, and community websites.
You can improve your chances of appearing in Local Packs and attracting local customers to your business by implementing these strategies.
Note: Formerly Google My Business (GMB) is now named as Google Business Profile (GBP).
Image SERP Optimization
Optimizing images enhances the visual appeal and user experience of your website. When users find relevant and visually appealing images in search results, they are more likely to click through to your website and engage with your content.
Image search provides an additional avenue for users to discover your website.
Optimizing your images for relevant keywords and ensuring they appear in image search results can attract new visitors and expand your audience.
Strategies for Image SERP Optimization
Implement the following strategies to optimize your website’s images for image SERPs:
- Optimize your images by compressing them to reduce file size without sacrificing quality. Use descriptive filenames that include relevant keywords, and provide alt text that accurately describes the image content. This helps search engines understand and index your images.
- Use high-quality images that are relevant to your content. Captivating and visually appealing images are more likely to attract clicks and engagement. Ensure that the images you use are original or properly licensed to avoid copyright issues.
- Provide descriptive captions for your images, as they appear in image search results. Surround the images with relevant text that provides context and supports the relevance of the image to the content on the page.
Additional Considerations for Image SERP Optimization
Keep the following considerations in mind when optimizing your website’s images for image SERPs:
- Create an image sitemap that lists the URLs of your website’s images. Submit the image sitemap to search engines to ensure that your images are properly indexed and appear in image search results.
- Implement schema markup, such as the “ImageObject” schema, to provide additional information about your images to search engines. This can help improve their visibility and presentation in image SERPs.
- Ensure that you have the necessary rights and permissions for the images you use on your website. If using images from other sources, provide proper attribution or link to the source to comply with copyright guidelines.
You can increase their visibility, attract more visitors to your website, and improve user engagement by optimizing your website’s images for image SERPs.
Video SERP Optimization
Video content has gained significant popularity among internet users, and optimizing your videos for video SERPs can help increase visibility, drive traffic, and engage your target audience.
Consider the following aspects of video SERP optimization:
Video has become a preferred medium for consuming information, entertainment, and educational content online.
Optimizing your videos for video SERPs allows you to tap into the growing demand for video content and reach a wider audience.
Videos have the ability to captivate and engage users, offering a dynamic and immersive experience. When your videos appear in video SERPs, they have a higher chance of attracting clicks, driving traffic to your website, and keeping users engaged.
Strategies for Video SERP Optimization
Implement the following strategies to optimize your videos for video SERPs:
- Optimize your videos by providing accurate and descriptive titles, tags, and descriptions that include relevant keywords. This helps search engines understand the content and context of your videos, improving their visibility in video SERPs.
- Create compelling and eye-catching video thumbnails that accurately represent the content of your videos. A visually appealing thumbnail can entice users to click on your video when it appears in video search results.
- Include transcripts and closed captions for your videos to make them accessible and searchable. Transcripts provide search engines with textual content to understand the context of your video, while closed captions enable users to consume your video’s content even in silent environments.
Additional Considerations for Video SERP Optimization
Keep the following considerations in mind when optimizing your videos for video SERPs:
- Optimize your video hosting platform, such as YouTube or Vimeo, by providing accurate and detailed information about your videos. Use relevant tags, categories, and descriptions to increase the visibility of your videos in platform-specific searches.
- Implement video-specific schema markup, such as the “VideoObject” schema, to provide additional information about your videos to search engines. This can enhance their visibility and presentation in video SERPs.
- Monitor and analyze video engagement metrics, such as views, watch time, likes, and comments. This data can provide insights into the performance of your videos and help you refine your video optimization strategies for better results.
You can increase their visibility, attract more viewers, and improve user engagement by optimizing your videos for video SERPs.
SERP Optimization for Mobile Devices
Mobile devices have become the primary means of accessing the internet, making mobile SERP optimization crucial for reaching and engaging a wide audience. Optimizing your website for mobile SERPs ensures a seamless user experience and improves your visibility in mobile search results.
Consider the following strategies for effective mobile SERP optimization:
Design your website with a responsive or mobile-friendly layout that adapts to different screen sizes and resolutions.
Ensure that text, images, and interactive elements are properly displayed and accessible on mobile devices.
Optimize your website’s loading speed for mobile devices.
Mobile users have little patience for slow-loading pages, and search engines prioritize fast-loading websites.
Compress images, minimize server response time, and leverage browser caching to improve page load speed.
Consider mobile-specific keywords that users are likely to search for on their mobile devices. Mobile searches often include location-based queries or voice search queries, so optimize your content accordingly to target these mobile-specific keywords.
Mobile SERP Features and Considerations
Mobile search results often feature different elements and considerations compared to desktop results.
Here are some key mobile SERP features and considerations to keep in mind:
- Mobile snippets are shorter summaries displayed on mobile devices. Craft concise and compelling meta descriptions that effectively communicate the relevance and value of your content in limited characters.
- Search engines have shifted to mobile-first indexing, where the mobile version of your website is prioritized for indexing and ranking. Ensure that your mobile website has the same content and relevant structured data as the desktop version to maintain visibility and rankings.
- If you have a mobile app, consider implementing app indexing to appear in mobile search results. App indexing allows your app’s content to appear as a deep link in search results, increasing visibility and driving app downloads and engagement.
Mobile Usability and User Experience
A seamless mobile user experience is paramount for mobile SERP optimization. Consider the following factors:
- Use responsive web design to ensure your website automatically adjusts to different screen sizes. This provides users with a consistent and user-friendly experience across various mobile devices.
- Optimize your mobile website’s navigation for ease of use. Implement clear menus, logical hierarchies, and prominent search functionality to help users find the information they need quickly and efficiently.
- Tailor your content for mobile consumption by using shorter paragraphs, bullet points, and concise headings. Ensure that font sizes are legible, and multimedia elements are optimized for mobile viewing.
You can effectively reach and engage mobile users, improve your search visibility, and provide a seamless mobile experience that encourages user interaction and conversions.
SERP Tracking and Analysis
SERP tracking refers to the process of monitoring and analyzing your website’s performance in search engine result pages (SERPs). It plays a crucial role in evaluating the effectiveness of your SEO strategies, identifying opportunities for improvement, and staying ahead of your competitors.
Here’s why SERP tracking is important:
By tracking your website’s rankings and visibility in SERPs, you can assess the impact of your SEO efforts. Monitoring changes in rankings allows you to identify which strategies are working and which need adjustment.
SERP tracking enables you to monitor your competitors’ rankings and performance.
You can adjust your own tactics to gain a competitive advantage by analyzing their strategies and identifying areas where they outperform you.
Tracking your website’s rankings for specific keywords provides valuable insights into their performance. You can identify high-performing keywords, discover new keyword opportunities, and optimize your content accordingly.
SERP Tracking Tools
Various tools are available to help you track and analyze your website’s performance in SERPs.
Consider using the following tools:
- Tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, and Moz offer rank tracking features that allow you to monitor your website’s rankings for specific keywords over time. These tools provide valuable data on keyword positions, search volumes, and trends.
- Utilize web analytics platforms such as Google Analytics to track organic search traffic, user behavior, and conversion rates. This data helps you understand the impact of your SERP performance on website traffic and overall business goals.
- Tools like Serpstat, SpyFu, and SimilarWeb provide in-depth analysis of SERPs, including competitor rankings, keyword opportunities, and search trends. These insights help you make informed decisions about your SEO strategies.
Actionable Insights from SERP Tracking
Analyzing SERP data can provide actionable insights to optimize your SEO efforts.
Consider the following actions based on your SERP tracking analysis:
- Identify underperforming keywords and optimize your content to improve rankings. Adjust your keyword targeting based on search volume, competition, and user intent.
- Analyze the content of top-ranking pages and identify opportunities to enhance your own content. Improve relevancy, readability, and value to better meet user expectations.
- Study your competitors’ top-ranking pages and understand their strategies. Identify areas where you can differentiate and outperform them, whether through content quality, user experience, or targeted keywords.
Regularly track and analyze your website’s performance in SERPs to adapt your SEO strategies, seize new opportunities, and stay ahead of the competition.
SERP CTR Optimization
SERP click-through rate (CTR) refers to the percentage of users who click on your website’s link in the search results after seeing it. Optimizing your SERP CTR is crucial for driving more organic traffic and improving your website’s visibility.
Consider the following aspects of SERP CTR optimization:
Crafting compelling meta titles and descriptions is essential for attracting clicks.
Write concise, persuasive meta titles that accurately represent the content of your page and entice users to click.
Craft informative and engaging meta descriptions that provide a compelling summary of what users can expect when they visit your page.
Utilize rich snippets and schema markup to enhance your search listings and make them more visually appealing.
Incorporate structured data to display additional information such as star ratings, reviews, pricing, and product availability, which can attract attention and increase the likelihood of clicks.
The position of your website in the search results significantly impacts its CTR.
Pages that appear higher in the rankings tend to receive more clicks. Focus on improving your website’s visibility and ranking through effective SEO strategies to increase the chances of attracting clicks.
Strategies for SERP CTR Optimization
Implement the following strategies to optimize your website’s SERP CTR:
- Conduct thorough keyword research and incorporate relevant keywords in your meta titles and descriptions. Tailor your messaging to align with user intent and create a strong connection between the search query and your content.
- Perform A/B testing with different variations of your meta titles and descriptions to determine which ones yield higher CTRs. Test different wording, calls to action, and formatting to find the most effective combination for attracting clicks.
- Include a clear and compelling call-to-action in your meta description to encourage users to click on your website. Use action-oriented language that creates a sense of urgency or promises a benefit to the user.
Monitoring and Optimization
Continuously monitor and optimize your SERP CTR to improve your website’s performance.
Consider the following actions:
- Use analytics tools to track and analyze your website’s CTR, click data, and conversion rates. Identify pages with low CTR and assess areas for improvement.
- Regularly review and refine your meta titles and descriptions based on performance metrics and user feedback. Experiment with different approaches to enhance their effectiveness in attracting clicks.
- Keep an eye on your competitors’ meta titles and descriptions. Identify strategies that are driving higher CTR for their listings and incorporate relevant tactics into your own optimizations.
You can increase the visibility of your website, attract more organic traffic, and improve the overall effectiveness of your SEO efforts by focusing on SERP CTR optimization.
Summary of the Topic
Understanding the structure and components of SERPs is crucial for effective online optimization. Each element, from the search bar to features like featured snippets and knowledge panels, shapes user experience and drives traffic. Knowing how search engines generate SERPs informs tailored optimization strategies.
This involves on-page and off-page SEO, technical considerations, and tracking with tools like Google Search Console.
Optimizing for local businesses, image and video SERPs, mobile devices, and improving click-through rates are essential components. Continuous monitoring and optimization can enhance visibility, attract traffic, and achieve business goals.
In short:
- Understanding SERP Components: Recognize the key elements of SERPs, including the search bar, search results, title tags, meta descriptions, URLs, People Also Ask section, rich snippets, knowledge panels, featured snippets, ad listings, local packs, site links, image and video carousels, news results, product carousels, social media profiles, and related searches.
- Process of Generating SERPs: Understand the step-by-step process, which includes crawling, indexing, ranking, and displaying results, with a focus on personalization to cater to individual user needs.
- Optimizing for SERPs: Implement on-page SEO factors like keyword research and optimization, content quality, and meta tags, along with off-page factors such as link building, social signals, and technical considerations like website speed, mobile-friendliness, and tracking tools for monitoring SERP performance.
- SERP Features and Rich Snippets Optimization: Learn to optimize for various SERP features like featured snippets by crafting concise summaries and knowledge panels through structured data markup.
- Local Businesses SERP Optimization: Focus on local SEO factors, image and video SERP optimization, mobile-friendly strategies, and tracking and analyzing SERP performance for continuous improvement.
- SERP CTR Optimization: Implement strategies to improve SERP click-through rates by monitoring and optimizing for higher visibility and user engagement.